Youth Empowerment for Climate Action and Community Development


About the Program
Youth Empowerment for Climate Action and Community Development is a comprehensive program aimed at equipping young people with the knowledge, skills, and resources to address climate change challenges. Through practical training in areas such as climate-smart agriculture, renewable energy, and environmental conservation, the program empowers youth to become leaders in sustainability. It promotes community engagement, creates green job opportunities, and fosters inclusivity, ensuring equal participation for both boys and girls. By developing leadership skills and promoting sustainable practices, the program contributes to both personal growth and community resilience
Values we live by
Our program is built on the values of empowerment and leadership, partnerships, mentorship and guidance, inclusivity and equal opportunities, and community engagement.
Be remarkable
Our program values emphasize empowering youth to lead, building partnerships for broader opportunities, providing mentorship for growth, ensuring inclusivity, and fostering community engagement for meaningful impact. These values drive sustainable and positive change.
Key Objectives and Areas of Focus
Empower youth with climate action knowledge
Empower youth with climate action knowledge by providing training on environmental sustainability and climate resilience practices.
Equip youth with practical skills
Equip youth with practical skills in climate-smart agriculture, renewable energy, and water conservation for sustainable livelihoods.

Promote environmental conservation
Promote environmental conservation through reforestation, biodiversity preservation, and community-led environmental initiatives.

Create sustainable job opportunities
Create sustainable job opportunities for youth by fostering green entrepreneurship and community-based enterprises.

Foster inclusive participation
Foster inclusive participation by ensuring equal opportunities for both girls and boys in leadership and climate action roles.

Build community resilience
Build community resilience by encouraging youth to engage in local decision-making and develop long-term climate adaptation strategies.
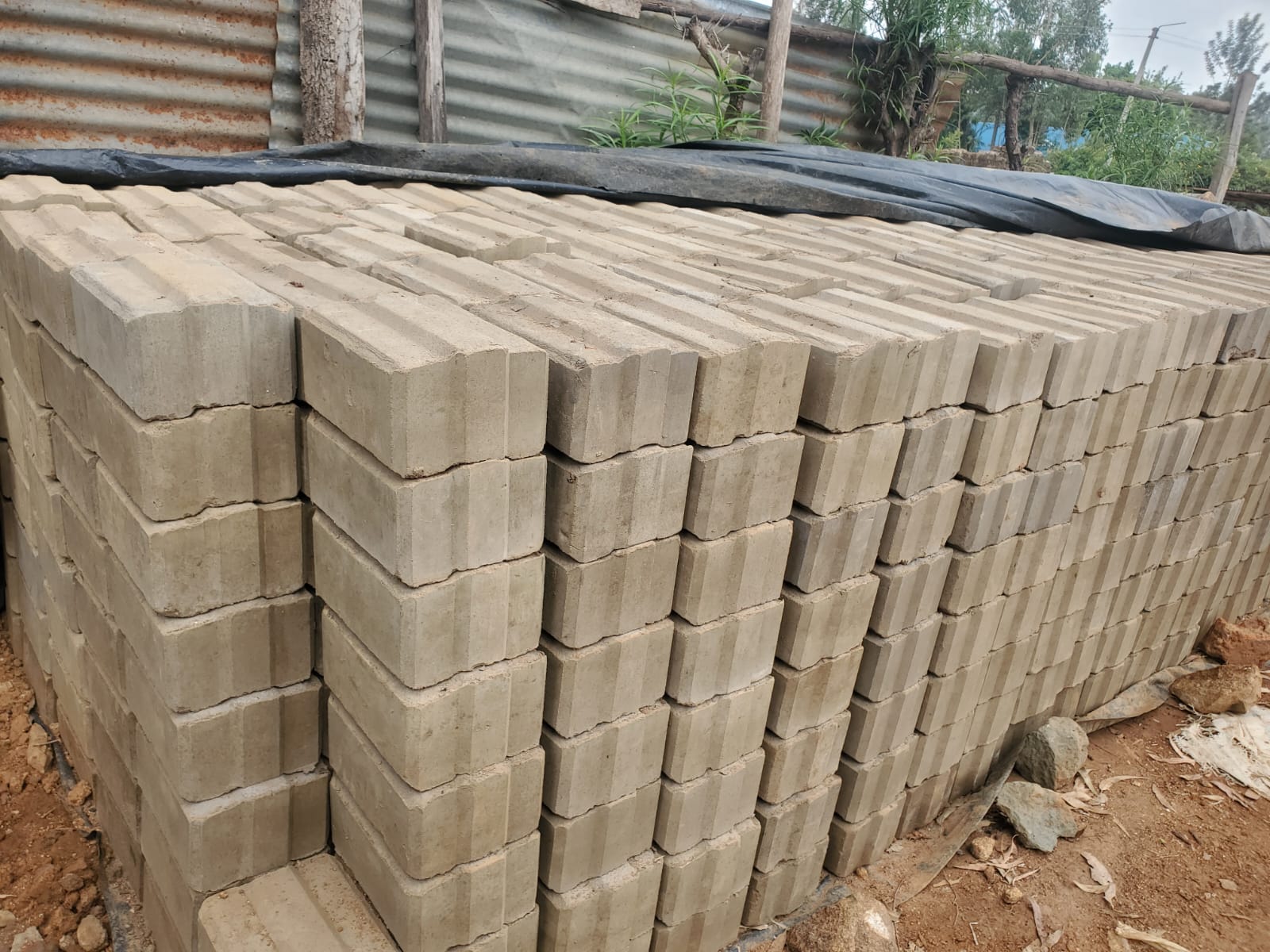
Project 01: Interlocking Soil Blocks.
Interlocking Soil Cement Blocks (ISCBs) are a type of construction material used for building walls, pavements, and other structures. These blocks are made by mixing soil, cement, and water, then compacting the mixture into molds to form blocks that interlock with one another.
The key feature of ISCBs is their interlocking design, which eliminates the need for mortar between the blocks. This design reduces construction time, labor costs, and the need for cement, which is typically used as mortar. The blocks’ interlocking feature allows for more efficient load transfer and stability, making them especially useful in regions where mortar or cement can be expensive or hard to come by.
Environmental Benefits of Using ISCBS.

-
Reduced Carbon Footprint: ISCBs use significantly less cement than conventional blocks, which are energy-intensive to produce. Unlike traditional fired bricks, there is no need for high-temperature burning during production, which drastically reduces energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, since ISCBs don’t require firing in kilns, this process doesn’t involve burning fuel, further lowering the carbon footprint.
-
Sustainable Use of Local Materials: The primary material in ISCBs is soil, which is often locally sourced. This minimizes transportation-related emissions since materials are easily accessible, reducing the need for long-distance hauling. The use of local materials also reduces the environmental impact linked to mining or manufacturing other building materials, which might harm ecosystems or require deforestation.
-
Minimal Water Usage: The production of ISCBs requires much less water compared to fired bricks, which often require large quantities of water for cooling and mixing. This makes ISCBs more water-efficient and less impactful on local water resources, which can be especially important in regions facing water scarcity.
-
No Burning, and Avoiding Deforestation: Traditional brick production often requires burning wood or other biomass in kilns to generate the necessary heat for firing bricks. This process leads to deforestation and contributes to the loss of biodiversity. By using soil and cement to create ISCBs, there’s no need to cut down trees for fuel. This not only preserves forests but also reduces the harmful emissions associated with biomass burning.
- Reduced Construction Waste: The interlocking design of ISCBs eliminates the need for mortar, reducing material waste during construction. Furthermore, there’s no need for additional chemicals or adhesives, which could have negative environmental effects. The efficient use of materials reduces both waste and the need for harmful substances in construction.
Sample Products and Demonstrations.

